|
Applications: 1. Optical Telecommunication 2. Tunable Lasers
3. Fiber Optic Sensors |
|
|
Tunable fiber gratings offer a versatile 'all-fiber' tunable optical filter
platform with the benefits of low-insertion loss and high-power handling
capabilities. They find applications in a wide range of fields, including
tunable lasers, nonlinear optics, quantum optics, fiber optic sensors, and
optical fiber telecommunications. |
|
|
Applications examples: |
|
|
1. Optical telecommunication, Nonlinear optics |
|
|
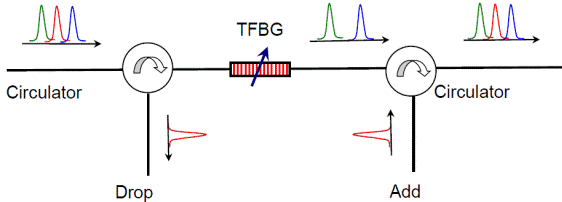
A tunable FBG can be paired with a
circulator, enabling the blocking of specific laser lines and the
transmission of other light signals, making it valuable for nonlinear optics.
A similar configuration is employed as a tunable add-drop filter in optical
telecommunication systems. Chirped FBGs find essential roles in managing
dispersion within high-speed wavelength-division-multiplexed (WDM) lightwave systems and ultra-fast laser systems. |
|
|
Fig.1. TFBG used as a tunable band-pass and band-reject
filter. |
Fig.2. TFBG used as a tunable add-drop
multiplexer and demultiplexer. |
|
2. Tunable Lasers |
|
|
Fiber lasers can emit laser light with
high-beam quality across a wide range of wavelengths efficiently. Leveraging
the broad gain bandwidth of active fibers, they offer an attractive option
for developing wavelength-tunable lasers. Traditional methods for achieving
wavelength tuning in fiber lasers often involve bulk optical filters or
diffraction gratings. However, these devices typically incorporate free-space
optical paths, resulting in high insertion losses and challenges in handling
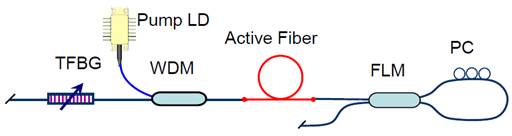
high power. Wavelength-tunable fiber lasers,
configured through direct tuning of the Fiber Bragg Grating, maintain
all-fiber connections internally, resulting in minimal cavity loss. This
configuration yields a simpler, compact, robust laser system that is highly
resistant to vibrations. Moreover, tunable FBGs are also
applicable in fiber-pigtailed semiconductor lasers for external cavity
wavelength tuning. |
|
|
|
|
|
Fig.3.
A tunable fiber laser, designed with an 'all-fiber' laser
cavity configuration . |
|
|
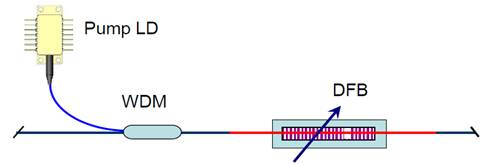
Fig.4. DFB single frequency fiber laser can be tuned by TFBG. |
|
|
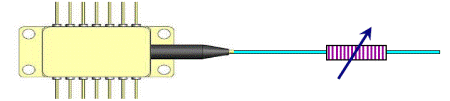
Fig.5. Fiber-pigtailed semiconductor laser can be tuned by TFBG. |
|
|
Fig. 6. Output
spectra from tunable fiber lasers at different wavelength bands. (a) Er-doped fiber laser; (b) Tm-doped fiber laser; (c) Yb-doped fiber laser. |
|